Pirfenidone (PFD) is an oral drug with antifibrotic properties.1 Its modes of action are not completely understood.2 The first results from studies using animal models support to the use of PFD in lung diseases primarily characterised by progressive fibrosis, and PFD is currently one of the two conditionally recommended drugs for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).3,4 IPF is the most common and by far the most aggressive type of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias, being associated with a severe prognosis with a median survival of 2–5 years for patients not receiving antifibrotic drugs.5,6 PFD has been recently evaluated in fibrosing lung diseases other than IPF, such as unclassifiable progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease, and is under investigation for other interstitial pneumonias.7–9 It has also been regarded with interest as a possible treatment for cardiac disorders where fibrosis plays an important pathogenetic role, such as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). This review provides an update on current and possible novel applications of pirfenidone.
Pharmacokynetics and Pharmacodynamics
PFD is a small synthetic molecule rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, with a half-life of about 3 hours.10,11 It is metabolised in the liver, mainly by cytochrome P450, and mostly excreted as the metabolite 5-carboxy-pirfenidone, either through the urine (80%) or in faeces (20%). PFD inhibits fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis by interfering with transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signalling and other growth factors, such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor.12,13 PFD also upregulates several matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that attenuate extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation.14 PFD also modulates acute inflammation by reducing the expression of inflammatory cytokines, most notably tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13, and by inhibiting the formation of the nucleotide-binding oligomerisation domain (NOD)-like receptor pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, a protein complex responsible for the recognition of stress signals and involved in the onset and maintenance of inflammatory responses.10,15 Finally, PFD may modulate the activity and proliferation of both T and B lymphocytes.10
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Possible Disease Mechanisms
The exact pathogenesis of IPF is still unknown, but its histopathological hallmarks have been well identified. This condition is characterised by areas of fibrosis alternating with relatively spared zones, honeycombing, and architectural distortion.16 Repeated microinjuries combined with an inability of alveolar epithelium to effectively repair wounds and epigenetic alterations lead to an aberrant activation of alveolar endothelial cells, which produce many profibrotic growth factors, chemokines, MMPs and procoagulant factors (such as tissue factor, activated factor VII, factor X and thrombin), all inducing the proliferation of fibroblasts and their differentiation into myofibroblasts. These last cells play a key role in the abnormal wound healing process, causing an exaggerated production of ECM, tissue scarring and irreversible lung fibrosis.17,18
TGF-β is probably the most important factor in IPF as it stimulates alveolar endothelial cells and fibroblasts, also through several microRNAs (miRNAs).19 Moreover, extracellular vesicles (small vesicles released by virtually all eukaryotic cells upon different stimuli and which can transport miRNAs), play an active role in intercellular communication, promoting the fibrotic response.20 Finally, some cells belonging to both innate and adaptive immune systems, such as dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages, T and B lymphocytes, with their associated cytokines, can still play a role in IPF pathogenesis.21
Pirfenidone in the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Possible Mechanisms
Antifibrotic Effects
Iyer et al. reported a protective effect of oral PFD towards bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis.1 Although bleomycin-induced fibrosis does not represent an accurate model of IPF, this was the first demonstration of potential antifibrotic activity of PFD in vivo. PFD was shown to effectively inhibit fibronectin and the production of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) which is an important factor in fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition, by human lung fibroblasts, when incubated with TGF-β. PFD also suppressed fibrotic changes, mediated by TGF-β, in human fetal lung fibroblasts.22,23 Another study confirmed that PFD reduced TGF-β-mediated α-SMA production by primary human lung fibroblasts and it effectively impaired phosphorylation of SMAD3 and phospho-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), two key effectors in the downstream of TGF-β signalling, thus providing a possible explanation for PFD antifibrotic effects in IPF.24 PFD can also act on heat shock proteins (HSP) and collagen overproduction. Indeed, PFD significantly inhibited HSP-47 and collagen I mRNA expression in a human type II alveolar epithelial cell line stimulated by TGF-β; moreover, cellular expression of fibronectin was reduced after pre-treatment with PFD.25 PFD has also been shown to be able to inhibit collagen fibril formation and assembly as well as inhibiting both PDGF and basic fibroblast growth factor, thus influencing myofibroblast differentiation or collagen I overproduction.26–28
Overall, these data show some potentially relevant mechanisms for the antifibrotic action of PFD, mainly focused on the inhibition of the TGF-β pathway.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
In a study using an orthotopic mouse lung transplant model, PFD treatment suppressed the activation of dendritic cells (DCs), which present antigens to T-cells, by several mechanisms including a PFD-mediated reduced response to Toll-like receptors agonists, PFD significantly reduced the production of several cytokines and chemokines, such as CCL2, TNF-α, CCL12 and IL-10, from stimulated DCs in vitro.29 In another study, PFD blunted T-cell proliferation and production of inflammatory cytokines.30 PFD has been shown to reduce the polarisation of alveolar macrophages (AMs) towards the M2 phenotype in rats; since M2-type AMs have profibrotic properties, mainly by secreting cytokines able to promote fibroblast proliferation, these findings could support a possible alternative mode of action for PFD.
In another murine model, PFD reduced airway responsiveness, inflammatory cytokines and cells in the bronchoalveolar fluid after pre-sensitisation with an allergen.21,31,32 Another study has demonstrated that PFD could reduce the production of proinflammatory cytokines by inhibiting p38 MAPK in B lymphocytes, thus representing a novel potential mechanism of action of PFD in lung fibrosis, since the inflammatory milieu induced by B-cell-derived cytokines can cause the activation and migration of fibroblasts.33
Clinical Trials on Pirfenidone for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
In 1999, Raghu et al. conducted the first open-label study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of PFD for patients with IPF.34 An open-label treatment was administered in terminally ill patients who had failed or not tolerated conventional therapy. The mortality observed was 22% at 1 year and 37% at 2 years, and PFD arrested the further decline of lung function in most patients. The drug was well tolerated with minimal side-effects that disappeared after it was discontinued or its dosage was decreased.34
A second open-label study was conducted in 2002 in patients with advanced IPF.35 Over 1 year of treatment, the deterioration in terms of chest radiographic scores, pulmonary function and arterial blood oxygen partial pressure (PaO2) appeared to stabilise, but survival was not significantly prolonged, probably because of the short treatment duration. As in the previous study, PFD was well tolerated.35
In 2005 a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase II trial tested the efficacy of PFD at a maximum dose of 1,800 mg/day in 107 patients with IPF.36 The primary endpoint – the change in the lowest oxygen desaturation (SpO2) during a 6-minute walking test (6MWT) – did not reach statistical significance (p=0.072), but PFD treatment demonstrated its efficacy in a few secondary endpoints, showing a significantly smaller decline in vital capacity (VC) (p=0.037) and preventing acute exacerbation of IPF at 9 months (p=0.003). The trial was prematurely stopped due to an excess of acute IPF exacerbations in the placebo group. Treatment with PFD was associated with more adverse events, not affecting the adherence to treatment.
In 2010, a phase III trial evaluated high doses (1,800 mg/day) and low doses (1,200 mg/day) of PFD in 275 patients with IPF.37 This trial demonstrated the efficacy of high-dose PFD treatment in slowing down VC deterioration (−90 ml versus −160 ml; p=0.042) and increasing the progression-free survival time (p=0.028) over 1 year. A lower but significant difference in VC decline was also seen in the PFD low-dose group (p=0.039). No statistically significant difference was detected in the mean change of the lowest SpO2 during a 6MWT. The incidence of adverse events was higher in the PFD treatment groups, without differences in treatment discontinuation.
Two Phase III international randomised double-blind placebo trials (CAPACITY 004 and CAPACITY 006), involving 779 patients with IPF, were performed in North America, Europe and Australia.38 The primary endpoint of both studies was the change in percentage predicted forced vital capacity (FVC%pred) from baseline to week 72. The CAPACITY 004 study included 435 patients treated with high-dose PFD (2,403 mg/day), low-dose PFD (1,197 mg/day) or placebo while the CAPACITY 006 study included 344 patients treated with exclusively high-dose PFD or placebo.
The CAPACITY 004 trial showed a significant difference in FVC%pred from baseline over 72 weeks between high-dose PFD and the placebo arm (−8% versus −12.4%; p=0.001). In the low-dose PFD group the mean change in FVC%pred was intermediate to that in the high-dose PFD and placebo groups. The high-dose PFD group also showed a positive result against placebo in terms of prolongation of progression-free survival. Instead, the CAPACITY 006 study recorded a significant difference in reduction in FVC%pred rate of decline up to week 48 in PFD group (p=0.005), but this difference was not maintained to week 72 (p=0.501). No significant effect was reported on progression-free survival, but high-dose PFD significantly reduced decline in 6MWT distance at week 72. The adverse effects, mainly gastrointestinal and skin-related events, were generally mild to moderate in severity, without any significant clinical consequence or reduction in therapy adherence.
Since the CAPACITY 006 study failed to meet its primary endpoint, another randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III trial was requested by US regulatory authorities, which was performed in 2014 to support the approval of PFD for IPF treatment.39 In the ASCEND trial, 555 patients with IPF were randomly assigned to receive PFD (2,403 mg/day) or placebo over 1 year. The PFD group showed a 50% reduction compared with the placebo group (17% versus 32%, respectively) in primary endpoint, which was a decline of at least 10% of the FVC%pred or death at week 52 compared to baseline. Furthermore, the proportion of patients with no decline in FVC increased by 133% in the PFD group (p<0.001). PFD-treated patients also displayed a relative reduction of 28% (p=0.04) in the decline of the 6MWT distance and a 43% longer progression-free survival (p<0.001). Gastrointestinal and skin-related side-effects were more common in the PFD group, but rarely caused discontinuation.39
In a pre-specified analysis of the pooled population of CAPACITY and ASCEND trials (1,247 patients), PFD significantly reduced the relative risk of all-cause mortality at 1 year by 48% (p<0.01) and the risk of IPF-related mortality at 1 year by 68% (p=0.006).40 Similarly, treatment with PFD at 2,403 mg/day reduced the proportion of patients with a decline of 10 percentage points or more in the FVC%pred or death by 44% and increased the proportion of patients with no lung function decline by 59%. PFD efficacy seemed to be independent of baseline disease severity.40,41
Even if the inclusion criteria for clinical trials do not necessarily reflect real-world patients and practices, emerging real-world data has shown that the tolerability and the overall efficacy of PFD on reducing FVC decline in patients with IPF were consistent with findings from the clinical trials.42–44
Pirfenidone and Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases
Diffuse interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) represent a large heterogeneous group of rare pulmonary disorders. ILDs arise from a large spectrum of distinctive aetiologies. They can be a pulmonary complication of connective tissue disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis and polymyositis, or result from the exposure to environmental antigens, such as chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis, or through occupational exposure, such as asbestosis, or due to unknown cause, such as idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and sarcoidosis.5 A variable proportion of patients with ILDs may have clinical features similar to IPF characterised by the decline of lung function, worsening of respiratory symptoms and health-related quality of life and higher mortality. In this case, they are termed progressive fibrosing ILDs or fibrosing ILDs with a progressive phenotype.45
Pharmacological studies with antifibrotic drugs have been conducted in patients with progressive fibrosing ILDs; both PFD and nintedanib have been used in fibrosing diseases secondary to connective tissue diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis associated with ILD and systemic sclerosis associated with ILD (SSc-ILD), as well as in unclassifiable fibrosing ILDs.
In 2016, the LOTUSS study evaluated the safety profile of PFD in patients with SSc-ILD, demonstrating an acceptable tolerability profile that improved as titration time increased.46 In 2020, Acharya et al. published a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled pilot study, where 34 subjects with SSc-ILD and an FVC%pred of 50–80% were randomised 1:1 to receive PFD (2,400 mg/day) or placebo for 6 months. Stabilisation/improvement in FVC was observed in 94% and 77% subjects in the PFD and placebo groups, respectively (p=0.33). The changes in FVC%pred, 6MWD, dyspnoea scores, modified Rodnan skin score (MRSS), and TNF-α and TGF-β levels did not differ significantly.47
Among chronic fibrosing ILDs, chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis may represent a diagnostic challenge with respect to IPF and its incidence is probably underestimated.48 An open-label study evaluated the efficacy and safety of PFD associated with prednisone and azathioprine with 22 people with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis enrolled and divided into two groups: 9 patients received only prednisone and azathioprine and the remaining 13 received combining PFD with prednisone and azathioprine. After 1 year of treatment, patients in the PFD arm did not show a significant improvement in FVC but they did have an improved quality of life with an acceptable safety profile.49
PFD has also been proposed in the treatment of COVID-19, both for the acute phase and the fibrotic sequelae.50 Four clinical trials on PFD and COVID-19 are currently recruiting new patients (NCT04653831, NCT04607928, NCT04856111 and NCT04282902).
Fibrosis in Cardiac Disease
Myocardial fibrosis is a common pathophysiological process in most heart diseases, defined as an excess of ECM deposition by cardiac fibroblasts.51 The activation of profibrotic pathways is a compensatory mechanism in response to myocardial damage and necrosis. Nonetheless, excessive ECM deposition may trigger a vicious cycle eventually leading to heart failure (HF).52 Fibrosis can be divided into two distinct forms: reparative or replacement fibrosis and reactive or interstitial fibrosis.53 While the first is generally observed in the development of an organised fibrotic scar after MI, the latter is a typically perivascular or interstitial fibrosis, as part of progressive pathological cardiac remodelling.53 Although the pathophysiological mechanisms leading to fibrotic remodelling differ according to the underlying disease, the cellular effectors are shared. Cardiomyocyte death or injurious stimuli, such as inflammation, often trigger fibrosis.54
Activation and conversion of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts are crucial points. The ECM proteins produced by myofibroblasts, such as collagens, glycoproteins and proteoglycans, offer local mechanical support to the failing heart in a multi-step process involving the degradation of damaged existing ECM, and the production, secretion and maturation of new ECM.53 Monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, mast cells, vascular cells and cardiomyocytes may also contribute to the fibrotic response by secreting profibrotic factors, such as inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, reactive oxygen species, proteases, endothelin-1, the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), and matrix proteins, such as TGF-β and PDGF.54
Following MI, the necrosis of cardiomyocytes triggers an inflammatory reaction, ultimately leading to replacement of dead myocardium with a reparative fibrotic scar.54,55 Ageing is associated with progressive fibrosis that may contribute to the development of increased wall stress, and diastolic and systolic ventricular dysfunction.56,57 Pressure overload-related fibrosis, caused by hypertension or aortic stenosis, is progressively associated with increased stiffness, diastolic dysfunction, ventricular dilation and HF.58 Volume overload due to valvular regurgitant lesions may also result in cardiac fibrosis.54 Chronic mitral regurgitation can result in left atrial enlargement and atrial fibrotic remodelling, which is one of the fundamental causes of persistent AF.59
Pirfenidone as a Possible Cardiac Protective Drug
As myocardial fibrosis is a key mechanism in the development of structural and functional cardiac alterations, therapeutic strategies targeting this process are becoming increasingly important. The heart diseases that will benefit most from anti-fibrotic therapies are the same where fibrosis plays a major pathogenic role, such as MI, AF and HF. A notable example is HFpEF. Following the systematic failure of trials on neurohormonal antagonists, researchers’ attention has shifted to the phenotypic heterogeneity of HFpEF, with the ultimate goal of developing therapies tailored on individual patient phenotypes.60 The new HFpEF paradigm states that coronary microvascular inflammation and myocardial fibrosis can be considered the central theme in the HFpEF conundrum, and antifibrotic drugs, such as PFD, may be effective tools in blocking this pathological mechanism.61
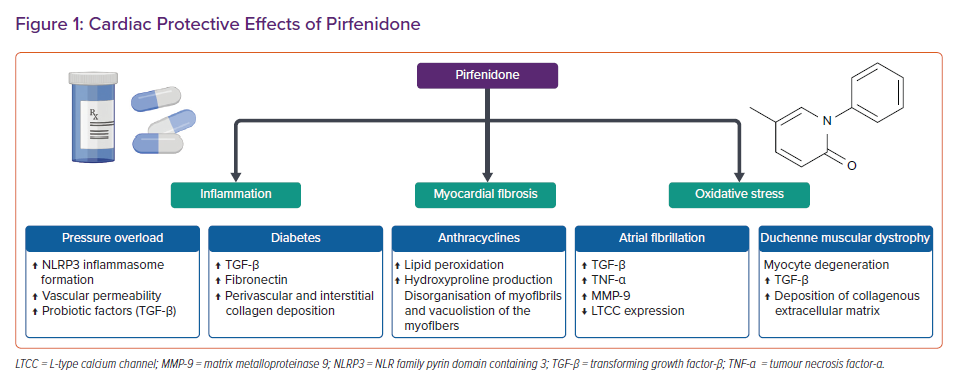
The following section summarises evidence about PFD’s antifibrotic activity in various animal models of cardiac disease, including pressure overload, diabetes and anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathies, MI, AF and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD; Figure 1).
Cardiac Protection in Animal Models
Pressure Overload
Myocyte hypertrophy and myocardial fibrosis are two key mechanisms of hypertensive cardiomyopathy. The increased deposition of collagen type I and III by cardiac fibroblasts in hypertensive hearts allows the force generated by hypertrophied myocytes to be transmitted to the entire ventricle.62 However, the excessive deposition of fibrotic tissue causes increased myocardial stiffness and diastolic dysfunction.63
TGF-β plays a crucial role because its increased expression is associated with an increased synthesis of collagen type I and III. The administration of an anti-TGF-β monoclonal antibody was reported to reduce fibroblast proliferation and fibrotic tissue deposition in pressure-overloaded rats.64 Additionally, inflammatory cells are found in the perivascular spaces of hypertensive hearts, suggesting that pressure overload might trigger an inflammatory response through inflammatory chemokines, such as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, followed by reactive fibrosis.62
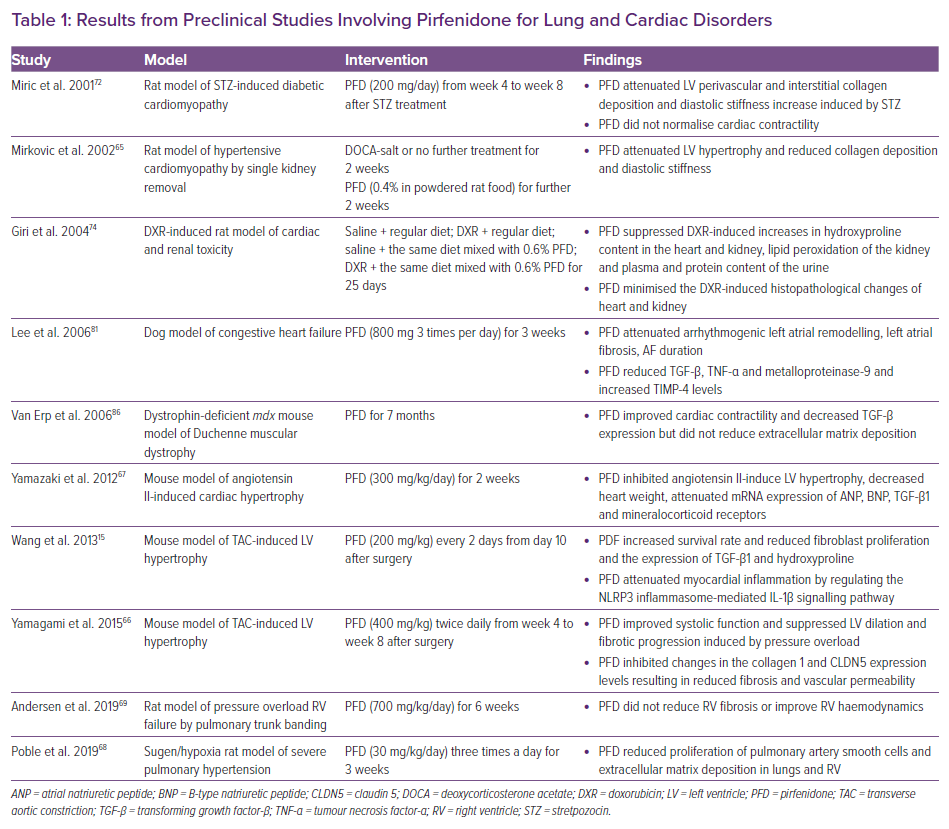
Multiple studies have shown that PFD might reduce vascular permeability in the acute phase and reduce the development of chronic fibrosis in pressure-overloaded hearts.15,65–67 Wang et al. investigated PFD in a mouse model of hypertensive left ventricular (LV) remodelling induced by transverse aortic constriction.15 They demonstrated that PFD attenuated myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation and fibrosis caused by NLRP3, a protein induced by pressure overload and involved in NLRP3 inflammasome formation. Furthermore, mice treated with PFD showed a higher survival rate compared with the control group.15
PFD was also studied in a rat model of hypertensive cardiomyopathy induced by unilateral nephrectomy followed by administration of salt and deoxycorticosterone acetate. Treatment with PFD for 2 weeks prevented cardiac remodelling by attenuating LV hypertrophy and reducing diastolic stiffness without lowering systolic blood pressure or reversing the increased vascular responses to norepinephrine.65
Similarly, PFD administration in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II infusion reduced LV hypertrophy and inhibited perivascular and interstitial tissue fibrosis.67 PFD reduced the expression of atrial and B-type natriuretic peptides, which are closely related to cardiac hypertrophy, and the levels of TGF-β1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Furthermore, PFD inhibited the expression of mineralocorticoid receptors, which implies it may prevent cardiac remodelling also by inhibiting the aldosterone signalling pathways.67
Another study investigated the effects of PFD on cardiac fibrosis in a pressure-overloaded HF mouse model, achieved by transverse aortic constriction.66 PFD reduced TGFβ-induced collagen 1 expression and increased the expression of claudin 5, a tight junction protein that regulates vascular permeability. These effects resulted in reduced fibrosis and reduced serum albumin leakage into the interstitial space.
The role of PFD in models of right ventricular (RV) pressure overload is controversial. PFD reduced RV fibrosis in a Sugen-hypoxia model of pulmonary hypertension.68 Conversely, Andersen et al. found that PFD did not reduce fibrosis or improve RV haemodynamics when the RV pressure overload was induced by pulmonary artery banding in a rat model.69
Diabetic and Anthracycline-induced Cardiomyopathies
Diabetic cardiomyopathy is characterised by structural and functional abnormalities, including systolic and diastolic dysfunction and LV hypertrophy.70 In this setting, cardiac fibrosis is partially due to increased expression of TGF-β1 caused by RAAS activation, oxidative stress, advanced glycation end-products, hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinaemia, although the specific mechanisms remain elusive.71 In a rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy, streptozotocin administration promoted interstitial collagen deposition in the kidney and the aorta, increased LV fibrosis and diastolic stiffness and reduced the maximum positive inotropic responses to norepinephrine and a calcium sensitiser in papillary muscles.72 PFD treatment reversed cardiac and renal fibrosis and improved diastolic function but did not normalise cardiac contractility or renal function.72
Cardiotoxicity is a well-recognised side-effect of several cancer therapies, especially anthracyclines, which are associated with myocardial oedema and fibrosis.73 Giri et al. investigated the protective role of PFD in a rat model of anthracycline-induced toxicity.74 PFD therapy attenuated the doxorubicin-induced increase in hydroxyproline content and the histopathological changes in the heart characterised by disorganisation and vacuolisation of cardiac myofibrils.74
MI
Cardiac fibrosis is a primary event following MI, which impairs cardiac function eventually leading to HF and may also act as a substrate for ventricular tachyarrhythmias.10,75,76 PFD therapy has shown to reduce fibrosis in a rat model of post-MI remodelling.66 Treatment was started 1 week after ischaemia-reperfusion injury and continued for 4 weeks. PFD-treated rats showed smaller infarct scars compared with controls, less total LV fibrosis, a reduced decline in LV ejection fraction (LVEF) and lower rates of ventricular tachycardia inducibility.77
In another rat model of MI, PFD administration by gavage for 4 weeks after permanent ligation of the left anterior descending artery reduced cardiac fibrosis and infarct size.75 The cardioprotective effects may be due, in large part, to an inhibition of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R)/p38 MAPK/RAS axis through the activation of liver X receptor-α (LXR-α).75 Similarly, in two different in vivo mice models of acute myocardial injury (induced by diphtheria toxin and closed-chest ischaemia-reperfusion injury), PFD attenuated LV remodelling and improved survival rates.78 Treatment with PFD had no effect on diphtheria toxin-induced cardiomyocyte cell death and the infiltration of neutrophils, monocytes or macrophages, but decreased CD19+ lymphocytes. B-cell depletion abrogated the beneficial effects of PFD. In vitro studies demonstrated that stimulation with lipopolysaccharide and extracts from necrotic cells activated B lymphocytes and PFD blunted this activation; therefore, PFD may also exert cardioprotective effects by modulating cardiac B lymphocytes.78
AF
Atrial interstitial fibrosis is a crucial element of structural and electrical remodelling, which plays a crucial role in the onset and perpetuation of AF.79,80 Indeed, fibrosis prolongs conduction times, leading to the creation of macro-reentrant circuits that increase susceptibility to AF and maintains AF.79 In a canine model of HF, PFD treatment reduced TGFβ, TNF-α and MMP-9 levels and increased the levels of an endogenous cardio-specific inhibitor of MMP, tissue inhibitor of MMP 4 (TIMP-4).81 These changes reduced atrial remodelling and AF development.70 PFD could also prevent AF by modulating the electrical properties of atrial tissue. Indeed, chronic treatment with PFD increased the expression of L-type calcium channels in adult rat cardiomyocytes. These channels are typically downregulated in AF; their increased expression by PFD prolongs both the action potential duration and the refractory period, thus lowering the susceptibility to AF.82
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
DMD is a severe, progressive, muscle-wasting disease caused by mutations in the DMD gene that abolish the expression of dystrophin in the skeletal muscle. Patients with DMD often develop systolic and diastolic dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis, often progressing to clinical HF.83,84 Indeed, dystrophin deficiency also causes cardiomyocyte degeneration and an increased deposition of ECM resulting in a progressive impairment of cardiac function.85
Van Erp et al. randomised 36 dystrophin-deficient mice to PFD or placebo for 7 months. PFD reduced TGF-β expression and improved cardiac contractility, but did not cause a significant reduction in myocardial fibrosis.86 The beneficial effects of PFD in this setting might then derive from a reduced synthesis of inflammatory cytokines and less oxidative stress more than an antifibrotic effect. Results from preclinical studies are summarised in Table 1.
Evidence of Cardiac Protection
Two clinical studies have retrospectively examined the effects of PFD on echocardiographic parameters of LV function. In the first, PFD treatment did not improve parameters of LV structure, diastolic function, systolic function and global longitudinal strain.87 In the second, PFD was associated with decreased indexed LV end diastolic and end systolic volumes, although no significant changes in LV diastolic, systolic function and strain were observed.88 However, both studies included only IPF patients and were limited by their small size and retrospective design.
To date, only one randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial included patients with a cardiac condition. The PIROUETTE phase 2 trial evaluated the safety and efficacy of a 52-week treatment with PFD in 94 patients with HFpEF (LVEF ≥45%) and myocardial fibrosis (defined as an ECM volume ≥27% measured by cardiac MRI [CMR]).89 At 52 weeks, the extracellular volume displayed an absolute decrease by 0.7% in the PFD group and an increase by 0.5% in the placebo group, with a between-group difference that was very small (also considering the variability in extracellular volume measurements by CMR), but still achieved statistical significance (between-group difference −1.21%; 95% CI [−2.12 to −0.31]; p=0.009). A limited but significant reduction in N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide values was also found. Conversely, no significant differences in measures of diastolic function, 6MWT nor Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire summary score values were observed.79 These findings suggested that PFD may be beneficial but further trials are needed to determine the clinical effectiveness and safety in a broader population.
Conclusion
PFD is an antifibrotic drug mostly studied in lung models. Solid evidence based on clinical trials and real-life studies shows that PFD improves the outcomes of IPF, slowing down or blocking the decline of respiratory function and improving survival. The therapeutic role of PFD in fibrosing ILDs, including SARS-CoV-2, is being evaluated. Furthermore, the antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activities of PFD provide a rationale for the evaluation of PFD for the treatment of chronic cardiovascular or renal diseases where fibrosis plays a crucial role. Following some promising results in animal models of several disorders, a phase II trial has recently reported a beneficial effect of PFD in patients with HFpEF, though limited to small changes in extracellular volume on repeated CMR scans.10 PFD was well tolerated, confirming the good safety profile emerging from studies on IPF.89 Further clinical studies on the efficacy and safety of PFD for the treatment of cardiac disease in humans are warranted.